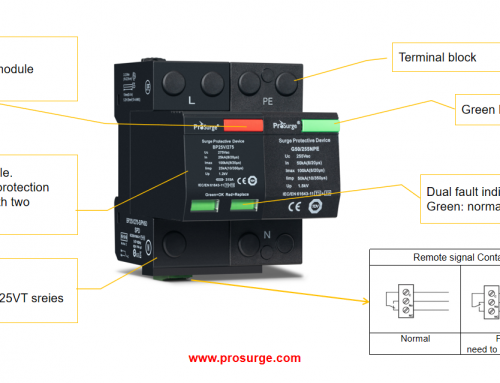
Surge Protection Device (SPD) is an electronic device that provides safety protection for various electronic devices, instruments, and communication lines. It is suitable for power supply systems with AC 50/60Hz and rated voltage of 220V/380V. The types and structures of surge protectors vary according to their different uses, but they can generally be classified in the following ways:
一、 Classified by working principle
- Voltage switch type: It is in a high impedance state when there is no instantaneous overvoltage, and suddenly changes to a low impedance state when a surge occurs, effectively diverting the surge current to ground and protecting the equipment from overvoltage damage. Commonly used nonlinear components include discharge gaps, gas discharge tubes, thyristors, etc.
- Voltage limiting type: It exhibits a high impedance state when there is no surge, but as the surge current and voltage increase, the impedance will continuously decrease, limiting the voltage to a safe level. Its current voltage characteristics are strongly nonlinear, thus avoiding damage to equipment caused by overvoltage. Commonly used nonlinear components include zinc oxide, varistors, suppression diodes, avalanche diodes, etc.
- Combination type: Combining voltage switch type and voltage limiting type SPDs together, it has both voltage switch function and voltage limiting function, which can simultaneously limit transient overvoltage and discharge surge current, providing better protection effect.
二、 Classified by application scenario
- Power protectors: including AC power protectors, DC power protectors, switch power protectors, etc.
- Signal protectors: including low-frequency signal protectors, high-frequency signal protectors, antenna feeder protectors, etc.
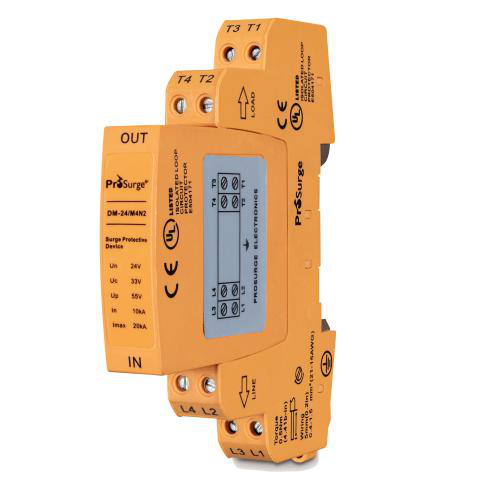
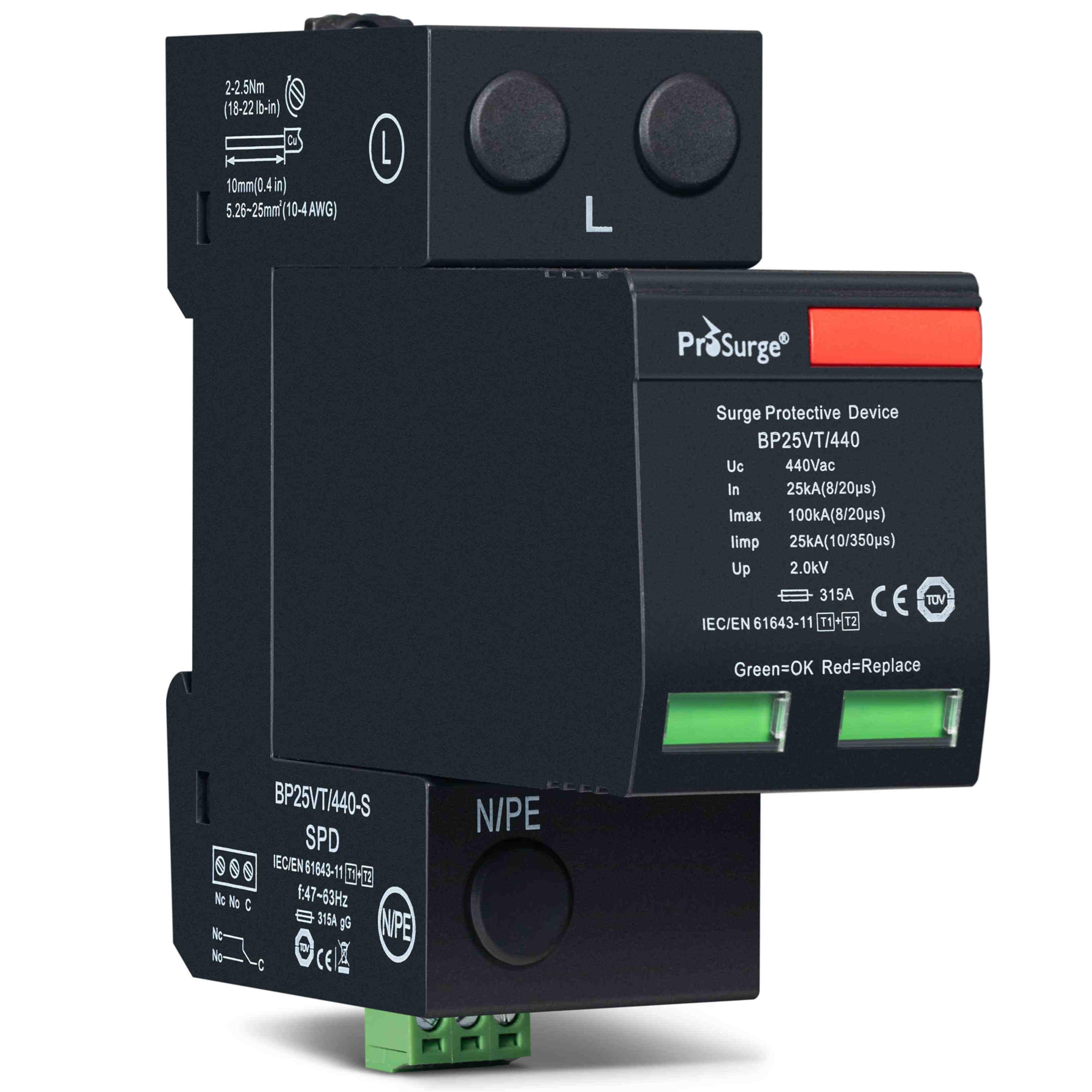


三、 Classified by experimental level
According to the national standard GB/T 18802.11-20201, surge protectors can also be classified into the following three categories based on test levels:
- Class I surge protector (first level surge protector):mainly used to withstand large impact currents caused by direct lightning strikes or induced lightning strikes, limiting them within the range that the equipment or system can withstand. The experimental waveform is 10/350 μ s
- Class II surge protector (secondary surge protector):mainly used to withstand medium amplitude surge currents caused by indirect lightning strikes or switch operations, further reducing them to a lower level. The experimental waveform is 8/20 μ s
- Class III surge protector (three-level surge protector):mainly used to withstand small amplitude surge currents or residual waveforms, and eliminate them to the minimum extent. The experimental waveform is a composite wave of 1.2/50 μ s and 8/20 μ s. The main application scenarios are sensitive equipment at the end of the line, such as computers, communication equipment, instruments, etc.
In addition, according to the suppression devices of surge protectors, they can also be classified into the following categories:
- Metal oxide varistor (MOV): composed of metal oxide (mainly zinc oxide) materials, it is a clamping device with characteristics very similar to two back-to-back connected voltage regulators, with a response speed of nanoseconds.
- Transient voltage suppressor (TVS):It operates in a voltage clamping mode with sub nanosecond response speed. There are multiple packaging methods that can meet the needs of different occasions. When the voltage on the TVS exceeds a certain amplitude, the device quickly conducts and releases surge energy through PN junction reverse overvoltage avalanche breakdown. Suitable for situations with small surge energy, if the surge energy is large and needs to be used together with other high-power surge suppression devices, it should be used as a secondary protection.
- Gas discharge tube (GDT):It is enclosed in a ceramic container and consists of two or more metal electrodes with gaps filled with inert gas (argon or neon). When the voltage applied to the two terminals reaches the point where the gas inside the gas discharge tube breaks down, the gas discharge tube begins to discharge, and the device enters a short-circuit state, so that the voltage across the electrodes does not exceed the breakdown voltage.
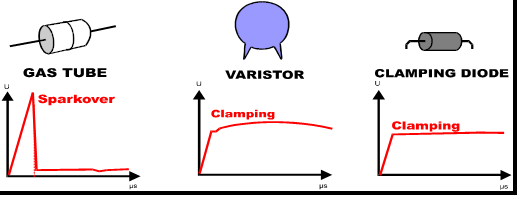
In summary, there are various types of surge protectors, which should be selected according to different application scenarios and protection requirements.